Smartphones
Smartphones
iPhone 16 Series Demand Strong, iPhone 16e Outperforms SE
L
Leakite
May 1, 2025
Smartphones
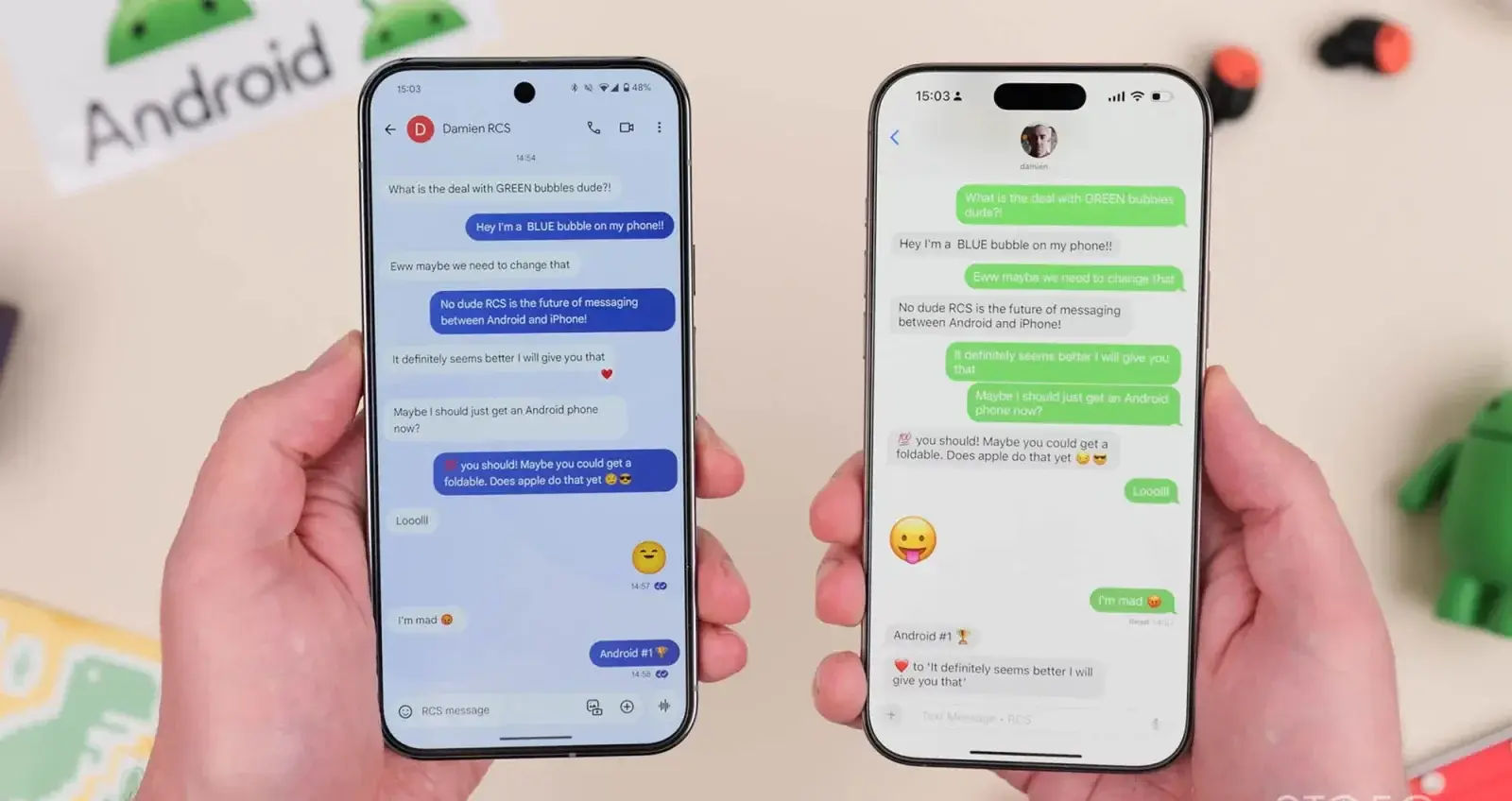
Encrypted RCS Messaging Coming to Xiaomi and iPhone
L
Leakite
April 4, 2025

Smartphones
Xiaomi Enhances Call Screen with HyperOS Update
L
Leakite
April 3, 2025

Smartphones
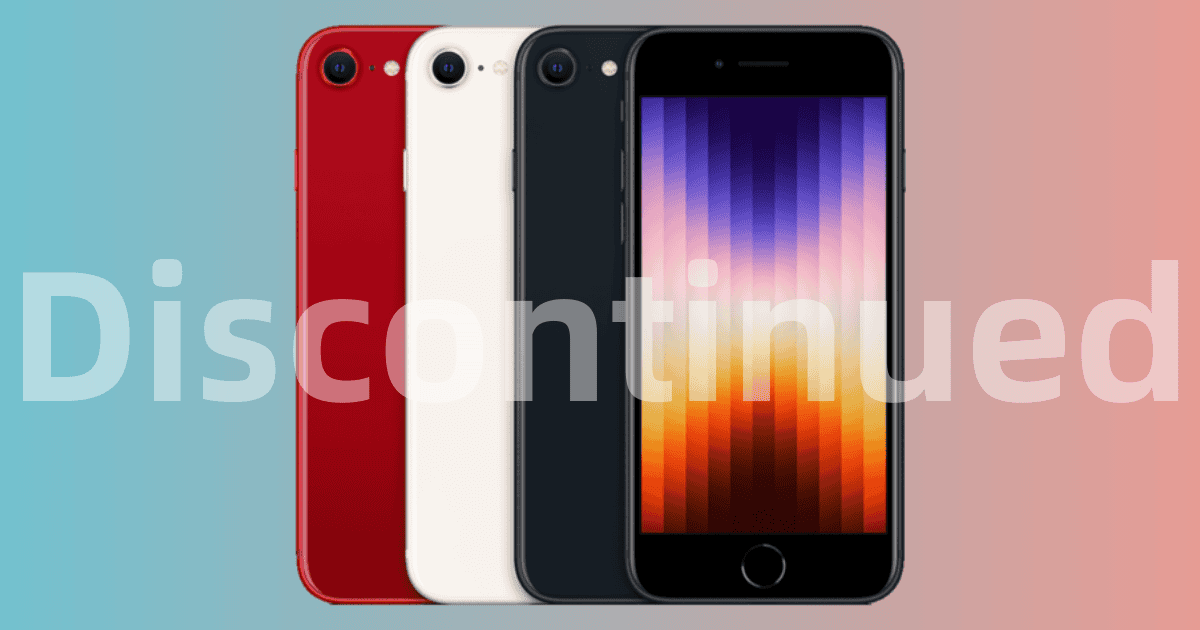
iPhone SE Discontinued: Why It's a Mistake for Apple
L
Leakite
April 3, 2025

Smartphones
iPhone 16 Series Launches in Indonesia After Sales Ban Lift
L
Leakite
April 3, 2025

Smartphones
Apple Streamlines Retail Leadership with New Global VP
L
Leakite
April 3, 2025
Smartphones
Pixel Screenshots App Gets Smart Suggestions
L
Leakite
April 3, 2025
Smartphones
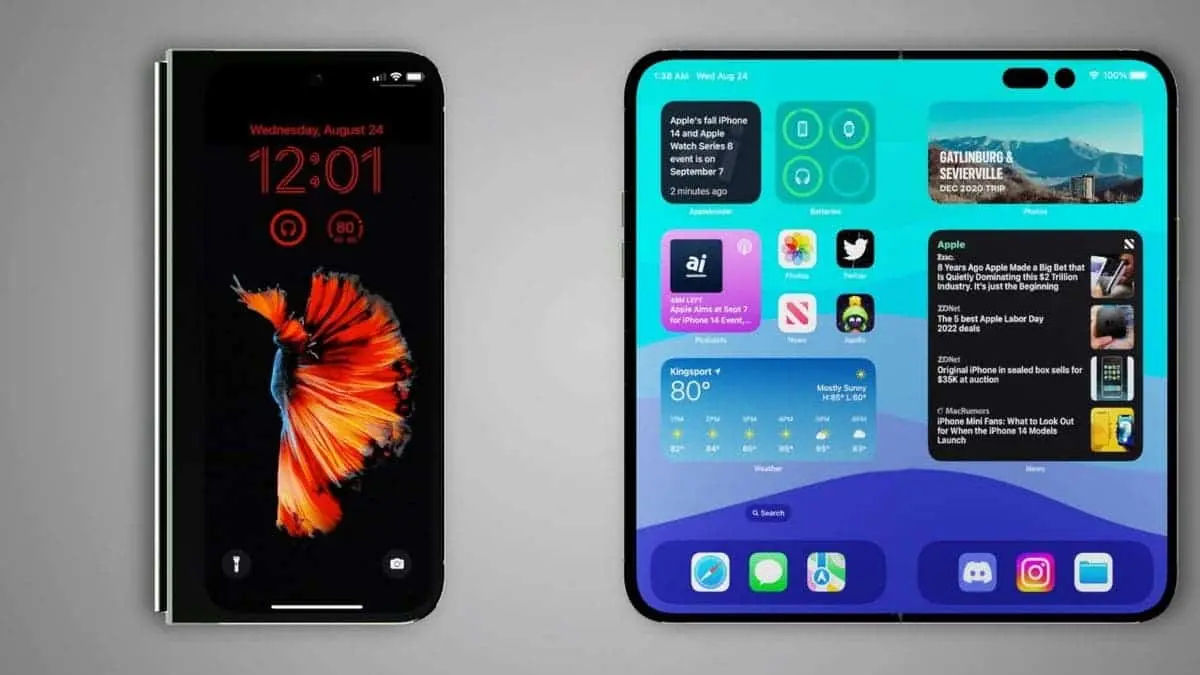
Apple's Foldable iPhone: Coming in 2026
L
Leakite
April 2, 2025

Smartphones
UMIDIGI's Next-Gen Smartphones Debut at 2025 Mobile Electronics Show
L
Leakite
April 2, 2025

Smartphones
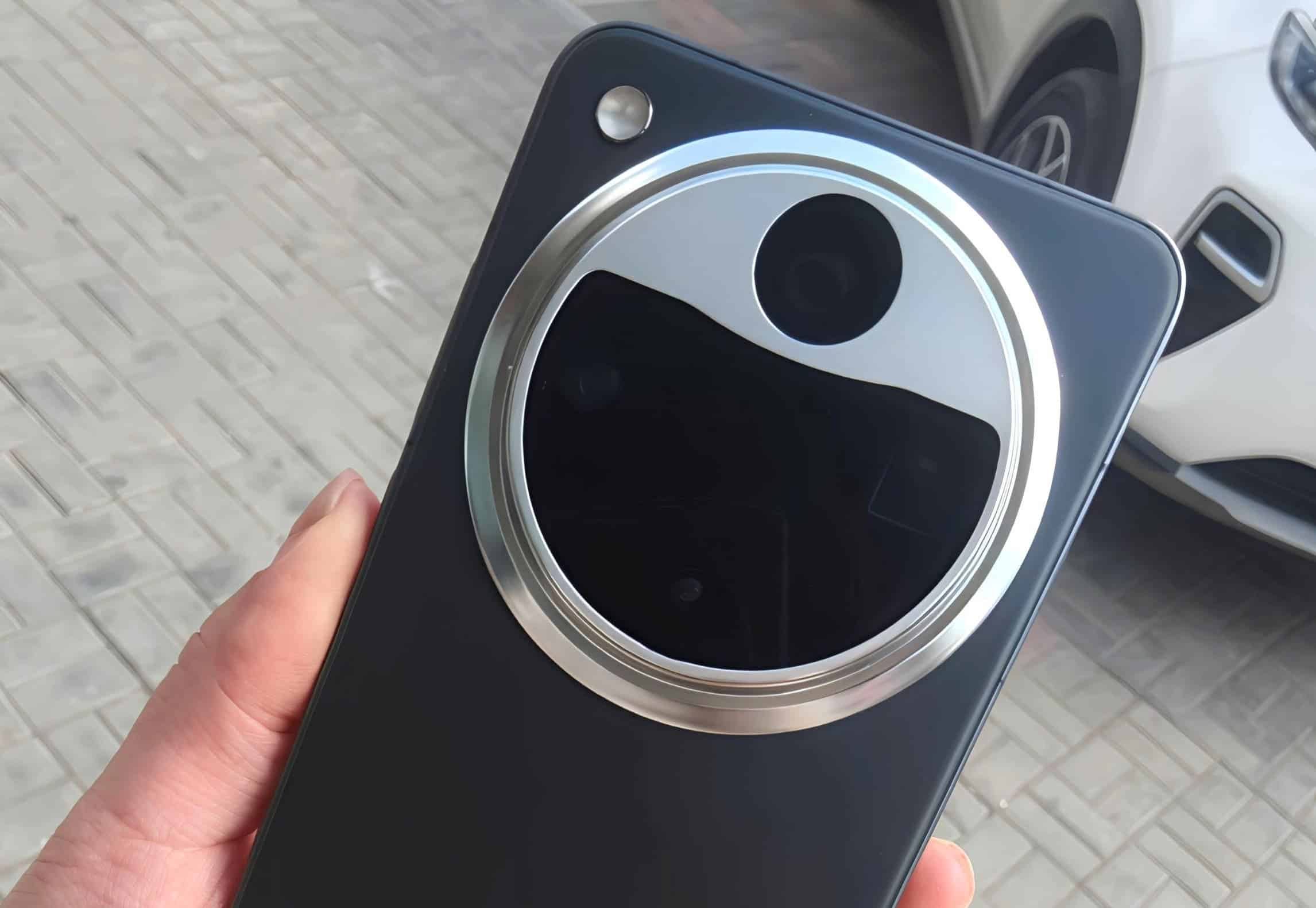
OPPO Find X8 Ultra: Powerful New Flagship Smartphone
L
Leakite
April 2, 2025